内置开放功能中的 a,a +,w,w + 和 r + 模式之间的区别?
在 python 内置的open w , a , w+ , a+和r+之间的确切区别是什么?
特别地,文档暗示所有这些都将允许写入文件,并表示它打开文件专门用于 “追加”,“写入” 和 “更新”,但未定义这些术语的含义。
答案
打开模式与 C 标准库函数fopen()完全相同。
BSD fopen联机帮助页对它们的定义如下:
The argument mode points to a string beginning with one of the following
sequences (Additional characters may follow these sequences.):
``r'' Open text file for reading. The stream is positioned at the
beginning of the file.
``r+'' Open for reading and writing. The stream is positioned at the
beginning of the file.
``w'' Truncate file to zero length or create text file for writing.
The stream is positioned at the beginning of the file.
``w+'' Open for reading and writing. The file is created if it does not
exist, otherwise it is truncated. The stream is positioned at
the beginning of the file.
``a'' Open for writing. The file is created if it does not exist. The
stream is positioned at the end of the file. Subsequent writes
to the file will always end up at the then current end of file,
irrespective of any intervening fseek(3) or similar.
``a+'' Open for reading and writing. The file is created if it does not
exist. The stream is positioned at the end of the file. Subse-
quent writes to the file will always end up at the then current
end of file, irrespective of any intervening fseek(3) or similar.我注意到,我不时需要重新打开 Google,只是为了构想两种模式之间的主要区别是什么。因此,我认为下一次阅读图会更快。也许其他人也会发现它也有帮助。
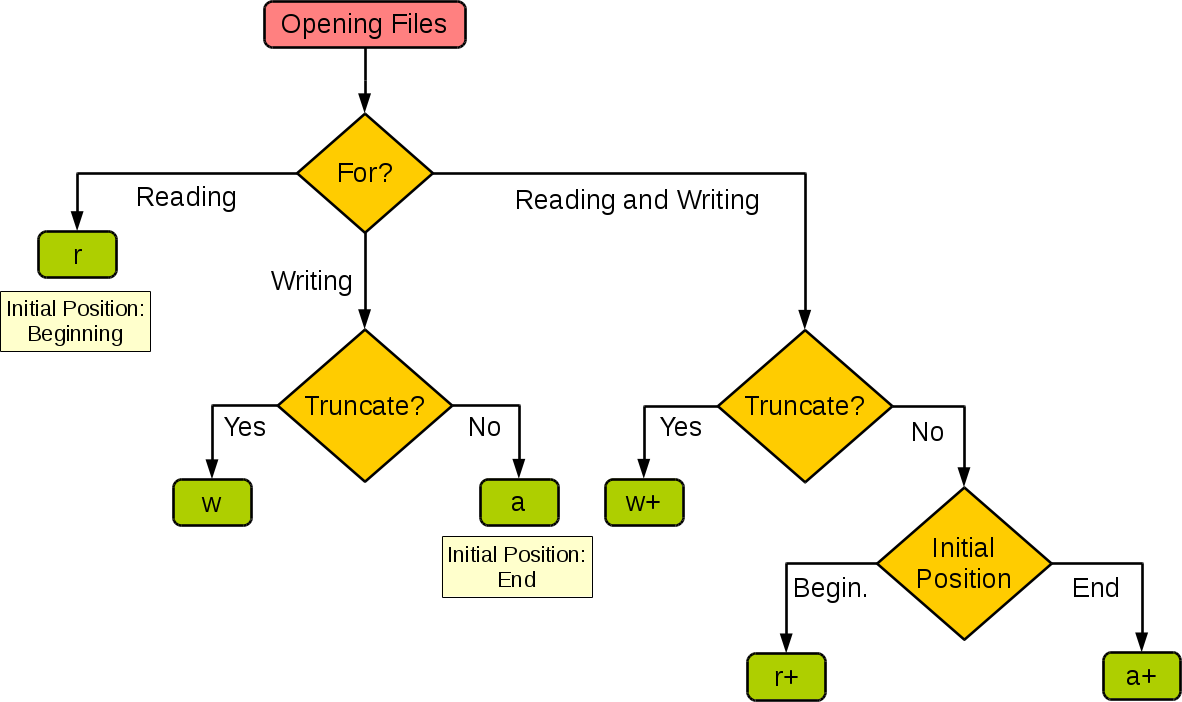
相同的信息,只是表格形式
| r r+ w w+ a a+
------------------|--------------------------
read | + + + +
write | + + + + +
write after seek | + + +
create | + + + +
truncate | + +
position at start | + + + +
position at end | + +意义在哪里:(为避免任何误解)
- 读取 - 允许从文件读取
写入 - 允许写入文件
create - 如果尚不存在则创建文件
截断 - 在打开文件期间将其清空(删除了文件的所有内容)
开始位置 - 打开文件后,将初始位置设置为文件的开始
- 末尾位置 - 打开文件后,将初始位置设置为文件末尾
注意: a和a+始终附加在文件末尾 - 忽略任何seek运动。
顺便提一句。至少在我的 win7 / python2.7 上,对于以a+模式打开的新文件而言,有趣的行为是:
write('aa'); seek(0, 0); read(1); write('b') - 忽略第二次write
write('aa'); seek(0, 0); read(2); write('b') - 第二次write引发IOError